Quickly set up GitHub SSH example
One of the most secure ways to communicate across the public internet is to use SSH. This is why GitHub SSH key setup is a top priority for users of the popular Git service.
Fortunately, the GitHub and SSH key configuration process is relatively straightforward, especially on a Linux distribution such as Ubuntu.
GitHub SSH key setup steps
To setup GitHub SSH keys and use them on Ubuntu, follow these steps:
- Create a GitHub SSH key pair with the ssh-keygen command
- Copy the value of the public SSH key to the clipboard
- Login to GitHub and navigate to your account settings
- Click on the SSH and GPG link
- Click Add Key to register the public SSH key with your account
- Name the key and paste the copied value into the text field
- Save your changes
- In your Git client, use the SSH based GitHub URL to clone your repo
Let’s go over each of these steps to setup GitHub SSH keys.
Create GitHub SSH keys
In Ubuntu, the SSH keys you create for GitHub must go in the .ssh folder. Perform all the GitHub SSH key create operation in this folder:
[email protected]:~$ cd ~/.ssh
Use the ssh-keygen command to create GitHub SSH key pairs:
[email protected]:~/.ssh$ ssh-keygen -o -t rsa -C "[email protected]"
The operation will prompt you to choose a location in which to save the public and private keys. Just click return to leave them in the .ssh folder. The SSH command will look here when a connection attempt is made to a remote server.
| Git with SSH keys tutorials |
|---|
| Need to configure SSH keys for GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket or CodeDeploy? These Git SSH key examples will help:
Follow these tutorials and you’ll learn to Git over SSH fast. |
The ssh-keygen command will also ask you to protect your GitHub SSH key with an optional passphrase. It’s permissible to leave the passphrase blank, so click return when prompted.
Here is the full output of when you issue the ssh-keygen command to create GitHub SSH keys:
[email protected]:~/.ssh$ ssh-keygen -o -t rsa -C "[email protected]" Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Your identification has been saved in /home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_rsa Your public key has been saved in /home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_rsa.pub The key fingerprint is: SHA256:g7RTuw9S+... The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 3072]----+ | ..Bo+.+o.. | |. *.= +E . . | | ...+ .. . . | | +.. ...+ o | | B o ++ S | | o . * = o + | | o B.oo . | | = oo + | | .o .o . | +----[SHA256]-----+
The purpose of the parameters used with the GitHub ssh-keygen command are as follows:
- The -o flag forces the tool to generate SSH keys with the OpenSSH format
- The -t flag specifies they type of SSH keys to create
- The -C flag allows for comments that get added as metadata at the end of the public key
GitHub SSH key location
When the GitHub SSH key create operation completes, the Ubuntu terminal will display a very satisfying piece of randomart.
You will also find public and private GitHub SSH keys in the current directory.
You will need to paste the contents of your public SSH key into GitHub. Cat the file to view its contents in the Ubuntu Terminal and then copy it:
[email protected]:~/.ssh$ cat id_rsa.pub ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQCwrUzqtm 3K9YNI2WbXxkcfnHZgyW7/3WXghBbKndhbKbCR00JLfTHsK Kaz17c4xIHQrw7u0GsPXai6pMtwMeVmXQH00L5hD0WE5Ioo
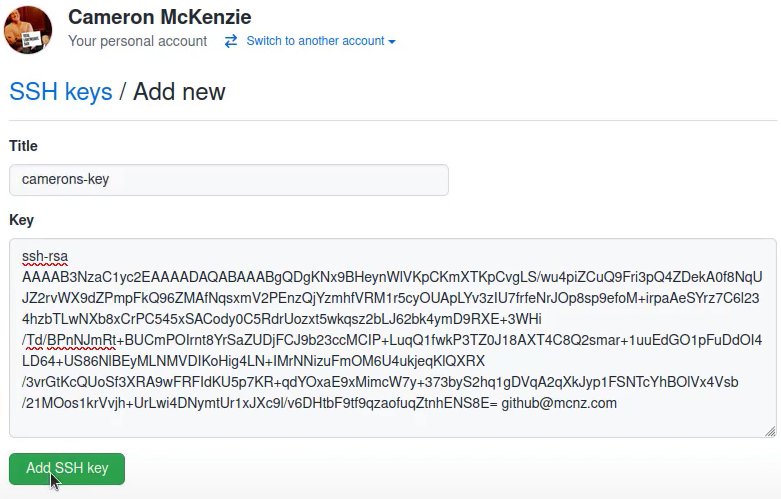
GitHub SSH key config
Next, you must configure the GitHub SSH key in the settings of your online account. Log into GitHub, navigate to your account settings, and find the link named “SSH and GPG keys.” Click on this link to create a new GitHub SSH key. Provide a unique name, and paste the value of the private GitHub SSH key you copied earlier.
With the GitHub SSH key setup complete, you can now use the SSH repository GitHub URL to clone from and push to your remote repo.
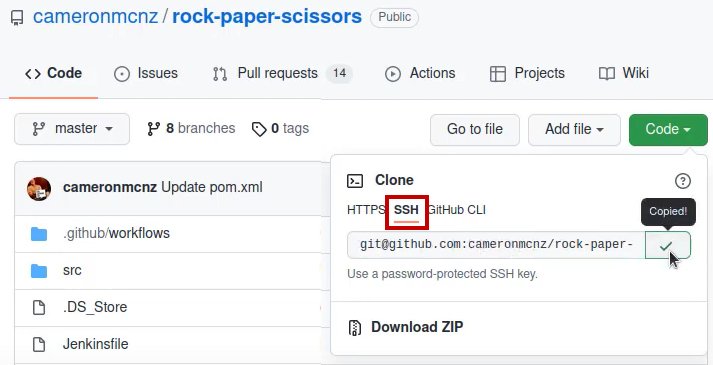
I will copy the SSH URL of my GitHub repository named rock-paper-scissors and then clone it in Ubuntu.
SSH Clone of GitHub repo
Once you copy the SSH URL of the GitHub repo, you can use it to clone a copy of the remote repo into the local environment.
On the initial clone, you might get a message that questions the authenticity of the host. This due to the lack of a third party certificate authority to validate your keys. If you are confident in the validity of the keys you just created — which you certainly should be, because you created them — just type yes to carry on with an SSH clone of the GitHub repo.
[email protected]:~$ git clone [email protected]:cameronmcnz/rock-paper-scissors.git
Cloning into ‘rock-paper-scissors’…
The authenticity of host ‘github.com (140.82.114.3)’ can’t be established..
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added ‘github.com,140.82.114.3’ (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Resolving deltas: 100% (206/206), done.
Now the GitHub SSH keys are set up properly and you’ve used them to clone the repository. You can continue to issue various Git commands with no worries about the underlying SSH config. All subsequent operations will use the existing setup of SSH keys for GitHub.
And that’s how easy it is to setup GitHub SSH keys in Ubuntu for Git.